GitHub SSO Provider
This section explains how to configure GitHub as an SSO provider in Localtonet and use it to protect your HTTP tunnels.
The setup consists of two main parts:
Creating an OAuth App in GitHub
Adding the GitHub provider to Localtonet
Step 1: Create an OAuth App in GitHub
Before adding GitHub as an SSO provider in Localtonet, you need to create an OAuth application in GitHub.
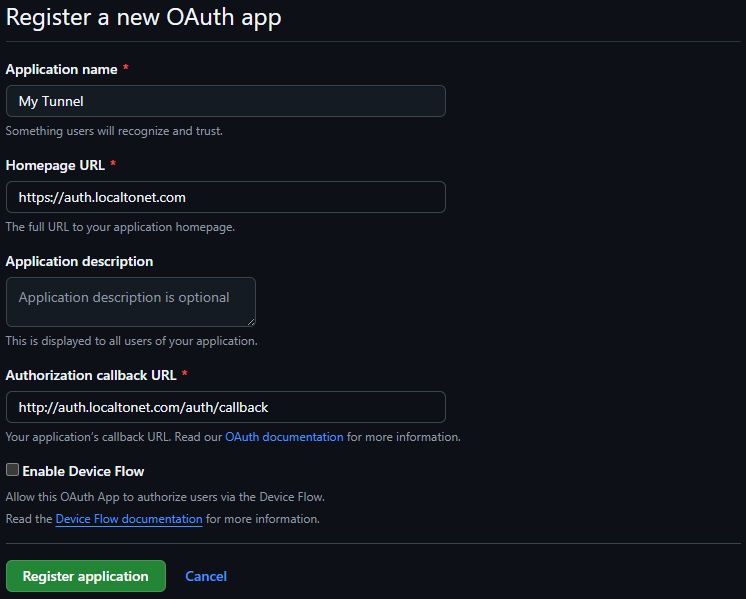
Click OAuth Apps → New OAuth App
Fill in the application details:
Application name
Any descriptive name (e.g.Localtonet Tunnel Access)Homepage URL
https://auth.localtonet.comAuthorization callback URL
http://auth.localtonet.com/auth/callback
Click Register application.
After creation, generate a Client Secret.
Copy the following values:
Client ID
Client Secret
You will use these values in the next step.
Step 2: Add GitHub Provider in Localtonet
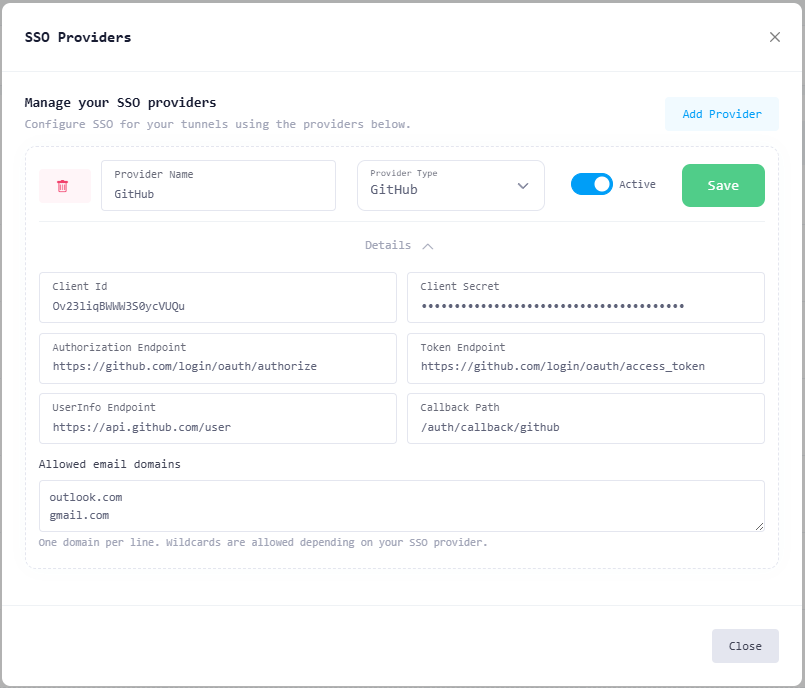
Open the SSO Providers setting in HTTP Tunnel page
Click Add Provider.
Fill in the provider details:
Provider Name
Any descriptive name (e.g.GitHub,Company GitHub Login)Provider Type
Select GitHubClient ID
Paste the Client ID from GitHubClient Secret
Paste the Client Secret from GitHub
The following endpoints are pre-filled automatically for GitHub and should not be changed unless you have a specific reason:
Authorization Endpoint
https://github.com/login/oauth/authorizeToken Endpoint
https://github.com/login/oauth/access_tokenUserInfo Endpoint
https://api.github.com/userCallback Path
/auth/callback/github
(Optional) Configure Allowed Email Domains
Enter one domain per line (e.g.
company.com)Only users whose verified email matches the domain will be allowed
Toggle Active to enable the provider.
Click Save.
Your GitHub SSO provider is now available for use.
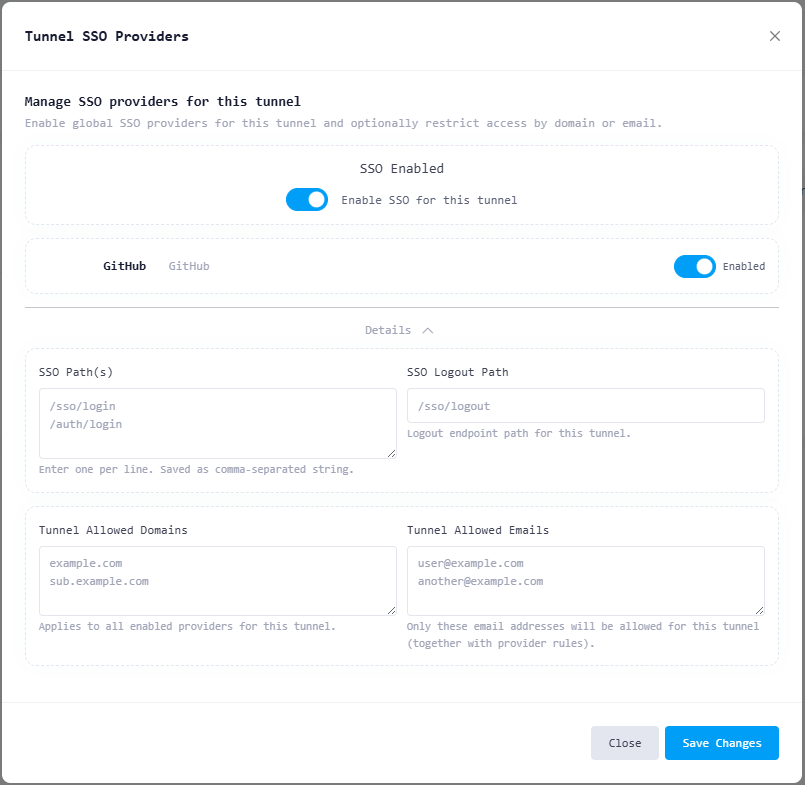
Step 3: Enable GitHub SSO for an HTTP Tunnel
Open the HTTP Tunnel Settings for the tunnel you want to protect.
Navigate to SSO Providers → Manage.
Enable SSO for this tunnel.
Toggle GitHub to enable it for this tunnel.
Configure optional tunnel-level restrictions:
SSO Path(s) – paths that require authentication
Logout Path – logout endpoint
Allowed Domains / Emails / Usernames – additional access control
Click Save Changes.
What Happens Next?
When a user accesses the tunnel URL:
The request is intercepted by the Localtonet authentication layer.
The user is redirected to GitHub for authentication.
After successful login, the user is redirected back to the tunnel.
Access is granted only if all provider and tunnel rules are satisfied.
The protected service remains unchanged.
Notes & Best Practices
GitHub authentication uses the user’s primary verified email
Use domain restrictions to limit access to organization users
You can enable GitHub alongside other SSO providers
Rotate Client Secrets periodically for security

